Things You Need to Know about Eczema
Eczema is a skin condition where some patches of skin get inflamed and become itchy, sore, rough, and cracked. In some cases, blood blisters may also occur. Eczema is not a single condition, but a group of conditions that include atopic dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, contact dermatitis, hand eczema, neurodermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and nummular eczema. This is a frustrating skin condition, where some people experience symptoms a few times a year while some deal with it on an everyday basis. Finding a soothing, natural eczema treatment can be life-changing for people suffering from this exasperating condition.
Some facts on eczema
- Certain food items, such as dairy products, nuts, etc.
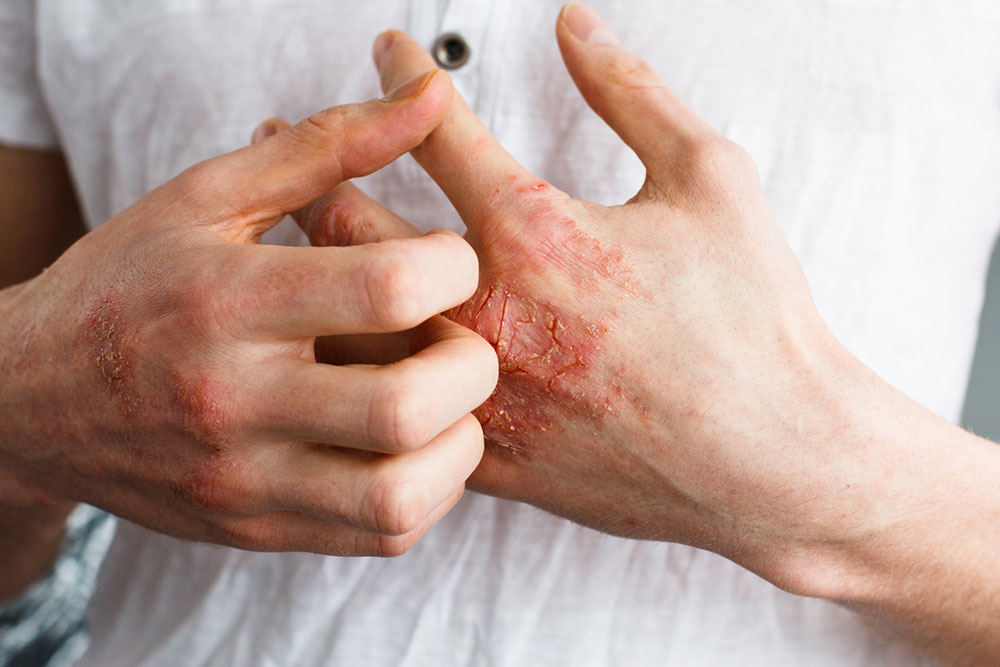
Symptoms of eczema
The symptoms of eczema range from mild to severe, and can change from one outbreak to another. Common symptoms include:
- The appearance of small bumps that may ooze out liquid
- Rough, dry and scaly skin that cracks
- Red or brown patches of skin on the face, hands, feet, wrists, neck, eyelids, ankles, upper chest or scalp
- Sensitive skin that gets swollen and inflamed from scratching
- A rash that causes intense itching and irritation
- Rashes due to atopic eczema
Best eczema treatment options
There is no complete cure for eczema.
Home remedies
There are various effective home remedies to manage eczema:
- Apply vegetable shortening
This thick and greasy kitchen product is one of the most effective ways to cure dry and scaly skin. - Add turmeric to your diet
Curcumin found in turmeric is an excellent antioxidant that aims to reduce the wound healing time. - Apply tea tree oil
Owing to its antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and nourishing properties, tea tree oil helps to reduce itching and soothe scaly skin. It is one of the best eczema treatments. - Consume Flaxseeds
Flaxseeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that help in blocking a chemical in the body, known as arachidonic acid, responsible for causing inflammation. - Fermented Cod Liver Oil
Fermented cod liver oil is a great source of healthy fats for the body. They help to decrease inflammation and lead to healthy cell and brain development. - Magnesium baths
These or other types of detox baths are extremely helpful in healing inflamed skin. Simply add 1-2 cups of magnesium flakes to ½ cup sea salt and ½ teaspoon natural vanilla extract. Add 10-15 drops of essential oil to this mixture and your homemade treatment for eczema is ready. - Probiotics
Consuming probiotics or probiotic-rich foods such as kefir, dark chocolate, raw cheese, miso, tempeh, etc., is believed to limit or reduce the number of eczema flares.
Medications
There are numerous medications that can be prescribed by the doctor for treating eczema. They include the following:
- Topical corticosteroid creams and ointments
These are a type of anti-inflammatory medications that are quite effective for relieving the itchiness, redness, inflammation and other symptoms related to eczema. They are directly applied to the skin. - Systemic corticosteroids
In case the topical ointments do not completely ease the symptoms, systemic corticosteroids are generally prescribed by the doctor. These are either consumed in the form of pills or injected into the body. However, their prolonged use is not recommended. - Antiviral and antifungal medicines
As the name suggests, they are helpful in treating viral and fungal infections. - Antibiotics
They are used to treat bacterial skin infections along with eczema symptoms. - Antihistamines
These cause drowsiness, thus reducing the risk of bedtime scratching. - Barrier repair moisturizers
These moisturizers intensely nourish the skin and keep it hydrated. - Topical calcineurin inhibitors
Calcineurin inhibitors suppress the activities of the immune system, thereby reducing inflammation and itching. - Phototherapy
This is one of the best eczema psoriasis treatments. It involves exposure to ultraviolet A or B, or sometimes both to subdue the activities of the immune system. The skin is carefully monitored throughout the procedure.
Even though eczema is not completely curable, you must adopt a proper line of treatment specific to your symptoms to ease the condition. Also, even after the area has healed, it is imperative to keep looking after it, to avoid further irritations.

